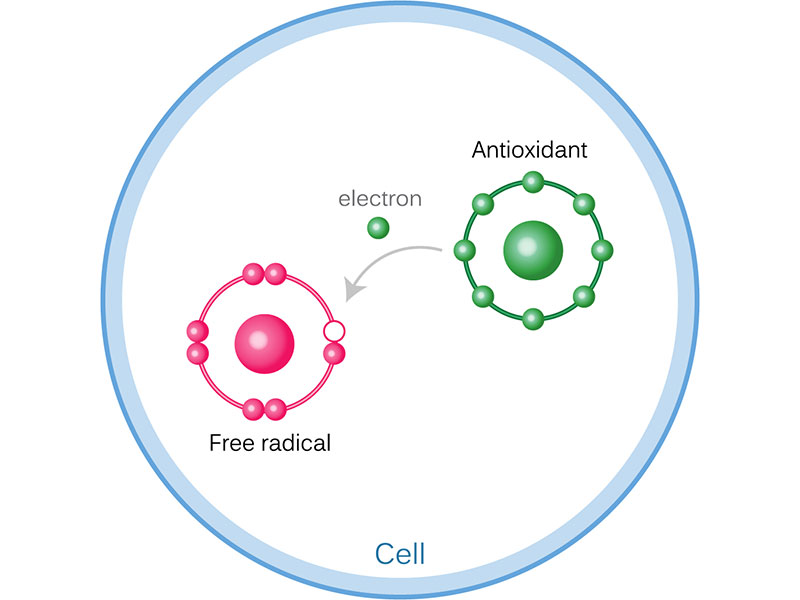
The protective antioxidant function of Coenzyme Q10 in neutralizing harmful free radicals is well known. How Coenzyme Q10 modulates the immune system is less well researched. The Brauner study suggests that Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves natural killer cell activity and reduces the extent of inflammatory processes.
What is the effect of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on the functioning of the immune system? We know that randomized controlled trials of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation have shown the beneficial role of Coenzyme Q10 in the prevention and adjuvant treatment of chronic heart failure and ischemic heart disease. We know that Coenzyme Q10 supplementation has been shown to be especially important for patients on statin medications and for middle-aged and elderly healthy individuals whose bodies no longer produce as much Coenzyme Q10 as in earlier years. What about Coenzyme Q10 supplements for patients whose immune system is weak?
Effects of Coenzyme Q10 on innate immune activity
Professor Annelie Brauner and a group of researchers at the renowned Karolinska University in Sweden have reported on the results of a clinical trial enrolling patients with diabetes, both type I and type II diabetes. The patients were all in their 50’s.
The researchers investigated the influence of Coenzyme Q10 supplementation on antimicrobial peptides and natural killer cells – both components of the innate immune system – in diabetes patients.
Supplementation with 2 x 100 mg Coenzyme Q10 daily
For 12 weeks, the Swedish researchers treated Type-I and Type-II diabetes patients with Coenzyme Q10 supplements – 100 milligrams twice daily with a meal. The Coenzyme Q10 supplement was the same supplement used in the Q-Symbio study of chronic heart failure patients and in the KiSel-10 study of healthy elderly citizens and in the Gulf War Illness study.
Significant increases in serum Coenzyme Q10 levels
The twice-daily supplementation raised the serum Coenzyme Q10 levels of the diabetes patients by a factor of 3.27. The effect was similar in both groups of diabetes patients.
Coenzyme Q10 and innate immune activity
Typically, immune system activity is characterized as being one of two types:
- innate immune activity
- adaptive immune activity
Innate immune system components are immune system cells that attack antigens in the body soon after the antigens appear. The foreign chemical properties of the antigens trigger the response of the innate immune system cells.
Adaptive immune system cells are cells that are produced and targeted against specific antigens. Consequently, their response time is slower than the response time of innate immune system cells.
Results of the Brauner study of Coenzyme Q10 and immune system activity
Coenzyme Q10 improves natural killer (NK) cell activity
Natural killer cells are white blood cells – components of the innate immune system – that reject tumor cells and cells infected by viruses. NK cells induce apoptosis to kill cells infected by viruses.
In the Brauner study, supplementation with Coenzyme Q10 was associated with the normalization/improvement of NK cell receptor levels and with an increase in NK cell activity.

Dr. William Judy at the International Coenzyme Q10 Association conference in Bologna, Italy. Dr. Judy says that the high concentration of reduced Coenzyme Q10 in the blood provides an immense protection of blood cells from oxidative stress and possibly prevents mutations of the white cells that result in leukemia.
Coenzyme Q10 reduces inflammatory processes
Human beta-defensin 2 peptides are anti-microbial peptides made by the white blood cells called neutrophils. The production of hBD2 peptides is usually induced by inflammatory processes that occur when microorganisms come in contact with epithelial cells.
In the Brauner study, supplementation with Coenzyme Q10 was associated with a decrease in the levels of hBD2 peptides. This result suggested that Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduced the diabetes-related inflammatory processes.
Conclusions from the Brauner study
The Swedish researchers noted that supplementation with Coenzyme Q10 improved NK cell activity and reduced hBD2 activity in Type-I diabetes patients. They concluded that Coenzyme Q10 treatment at the level of 100 milligrams twice daily supports the innate immune system in Type-I diabetics and may help to prevent late complications in Type-I diabetes patients.
Lifestyle choices important to counter genetic risk of disease
Lifestyle choices can induce many physical and oxidative stresses in the body. Many of these lifestyle choices can be factors in causing the mutation of genes and the subsequent development of degenerative diseases.
- To smoke or not
- To exercise or not
- To eat a healthy diet (fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains) or not
- To take a daily Coenzyme Q10 supplement or not
Coenzyme Q10 supplements an easy choice
Coenzyme Q10 supplements are safe, affordable, and easy to take. So, why risk not having enough Coenzyme Q10 as you get older?
Sources:
Brauner, H., Lüthje, P., Grünler, J., Ekberg, N. R., Dallner, G., Brismar, K., & Brauner, A. (2014). Markers of innate immune activity in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and the effect of the anti-oxidant Coenzyme Q10 on inflammatory activity. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 177(2), 478-482.
Ravaglia, G., Forti, P., Maioli, F., Bastagli, L., Facchini, A., Mariani, E., & … Lenaz, G. (2000). Effect of micronutrient status on natural killer cell immune function in healthy free-living subjects aged > 90 years. The American Journal Of Clinical Nutrition, 71(2), 590-598.



Leave A Comment