Coenzyme Q10 supplementation has beneficial effects on glucose control, also known as glycemic control. The benefit of the CoQ10 supplementation is especially apparent in diabetes
patients. Results from a meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials show that taking 100-200 mg/day of Coenzyme Q10 achieves the greatest benefit for glucose control [Liang 2022].

The q10facts.com guest author this week is Dr. Ross Pelton, the natural pharmacist, whose book Rapamycin is available on amazon.com. Please visit Dr. Pelton’s website at https://naturalpharmacist.net/.
How many of us have heard the cardiologist say: “Cut back on your sugar intake”?
There is a good reason for this advice. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and disability in the world today. Frequently, it is glucose metabolism disorders that are driving the development of cardiovascular diseases [Liang 2022].
Note: The term glucose metabolism refers to the process of breaking down of sugars, e.g., glucose, and converting the glucose to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy units.
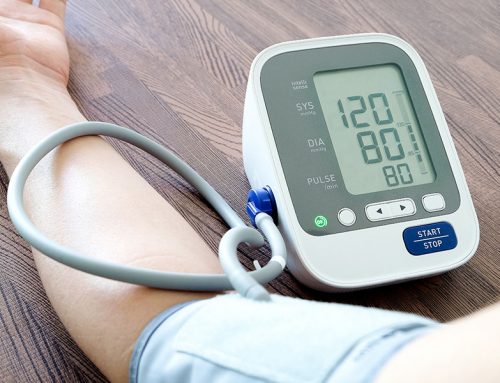
Note: Glucose control is the process of maintaining a blood glucose level that is safe and non-diabetic, which is a blood glucose level between 70 and 130 milligram/deciliter before meals and less than 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal [AHRQ 2017]. To convert the above mg/dL values to millimol/liter values, we divide by 18. So, normal blood glucose levels are about 3.9 to 7.2 mmol/L before meals and less than 10 mmol/L two hours after a meal. The 5.3 mmols per liter depicted here are within the normal range.
The Effects of CoQ10 Supplementation on Glucose Control
In 2022, Liang et al reported the results of a meta-analysis of the data from 40 studies that had enrolled 2,424 participants.
They found that the CoQ10 supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels, fasting blood insulin levels, and HOMA-IR insulin resistance values.
They observed a U-shaped dose-response relationship that showed that daily supplementation with 100 to 200 mg of Coenzyme Q10 most effectively reduced fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR values [Liang 2022].
In the meta-analysis, the CoQ10 supplementation benefited glucose control in individuals with diabetes even more than it did non-diabetic individuals [Liang 2022].
Conclusion: CoQ10 Supplementation Benefits Glucose Control
- In the CoQ10 research literature, there is an impressive number of randomized controlled trials – 40 with a total of 2,424 study participants – that address the question of how Coenzyme Q10 affects glucose control.
- There is good scientific evidence that daily CoQ10 supplementation doses of 100-200 mg promote good glucose control [Liang 2022].
- Better glucose control should reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
- Not all CoQ10 supplements give equally good absorption. Much depends on the manufacturer’s formulation. In fact, many commercially available CoQ10 products have quite low absorbability because of the formation of crystals. I only recommend crystal-free CoQ10 products.
Sources
AHRQ. Glucose Control Factsheet. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2017. Retrieved from https://www.ahrq.gov/hai/tools/surgery/tools/surgical-complication-prevention/glucose-control-factsheet.html.
Liang Y, Zhao D, Ji Q, Liu M, Dai S, Hou S, Liu Z, Mao Y, Tian Z, Yang Y. Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on glycemic control: A GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Aug 3;52:101602.
The information presented in this review article is not intended as medical advice and should not be used as such.




Leave A Comment